
Your data, our passion.
Snack-Sized Data Basics
SQL - Table Creation
As we've seen in the previous lesson, to create a table, we need:
-
the SQL keyword required to create a table
-
the table name
-
the column names
-
the column data types
-
and the column constraints if any
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column_name_1 DATA_TYPE COLUMN_CONSTRAINT,
column_name_2 DATA_TYPE,
column_name_3 DATA_TYPE
);
Let's create a table called students to store student information.
CREATE TABLE students (
student_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
date_of_birth DATE NOT NULL,
allergies VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT 'None'
);
Let's break it down.
-
CREATE TABLE is the standard SQL command for creating a table.
-
students is the name we’ve chosen for our table. This is user defined, so you can name it anything.
-
The parentheses ( ) enclose the table’s columns.
-
student_id is our first column. We use SERIAL to automatically generate a unique number for each record, and PRIMARY KEY to ensure that every student_id is a unique non null value.
-
first_name and last_name use VARCHAR(50). This allows flexibility in name lengths without requiring exactly 50 characters, while also providing enough storage for longer names. We use NOT NULL to ensure that the first and last names are always provided.
-
date_of_birth is stored as a DATE type, which ensures proper date formatting. The NOT NULL constraint ensures that a date of birth is always recorded.
-
allergies is stored as VARCHAR(100), providing enough space for listing allergies. If no allergies are specified, the system inputs "None".
-
Finally, the semi colon ; is used to terminate the query.
Now, head over to sqliteonline.com and connect to the PostgreSQL database by selecting PostgreSQL from the left menu, and click Click to connect. Refer back to the getting started section if needed.
Practice creating the table above, and try designing other tables of your own. Experiment with different data types and constraints.
You can have several queries within your query editor, but to run a given query, you can simply select it, then click Run .
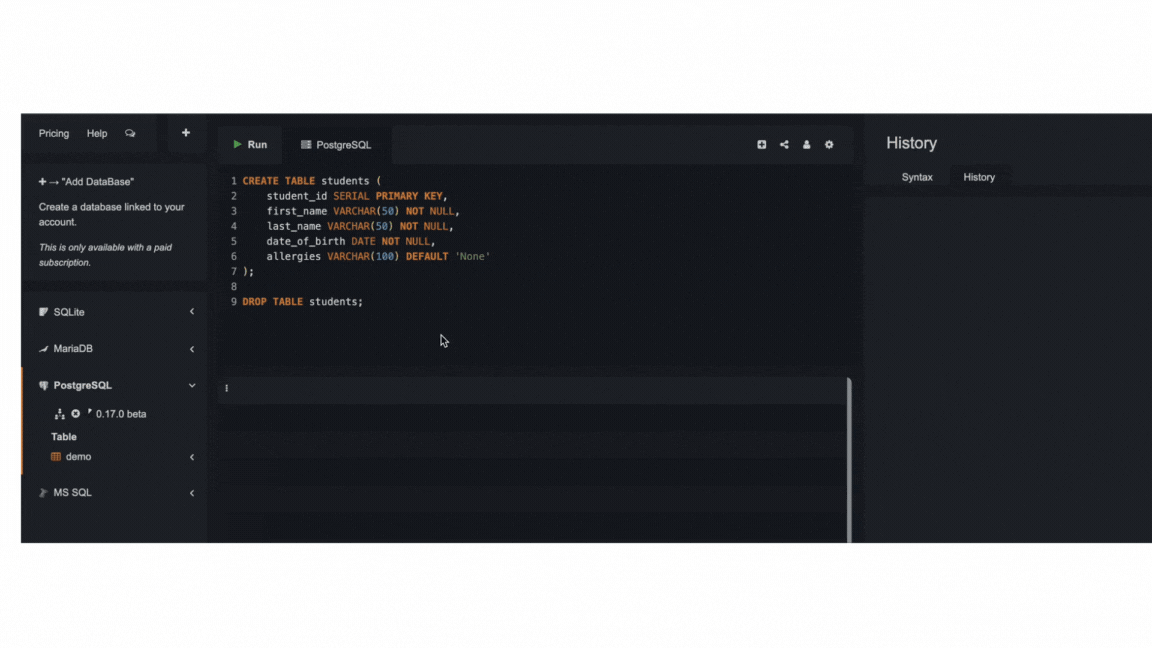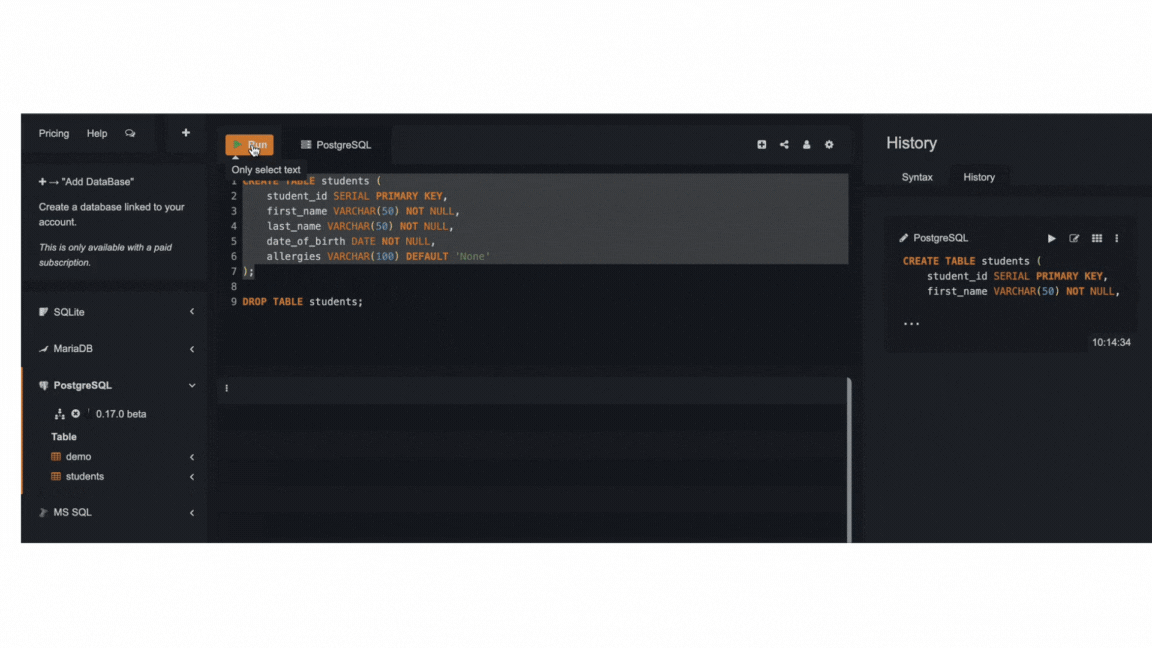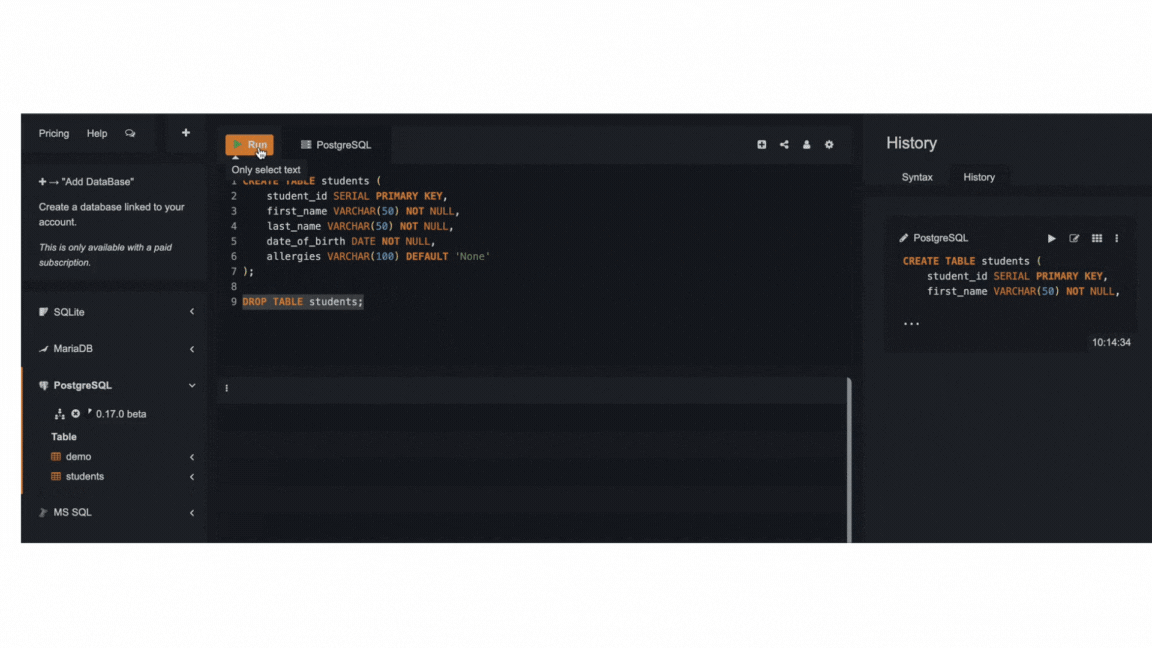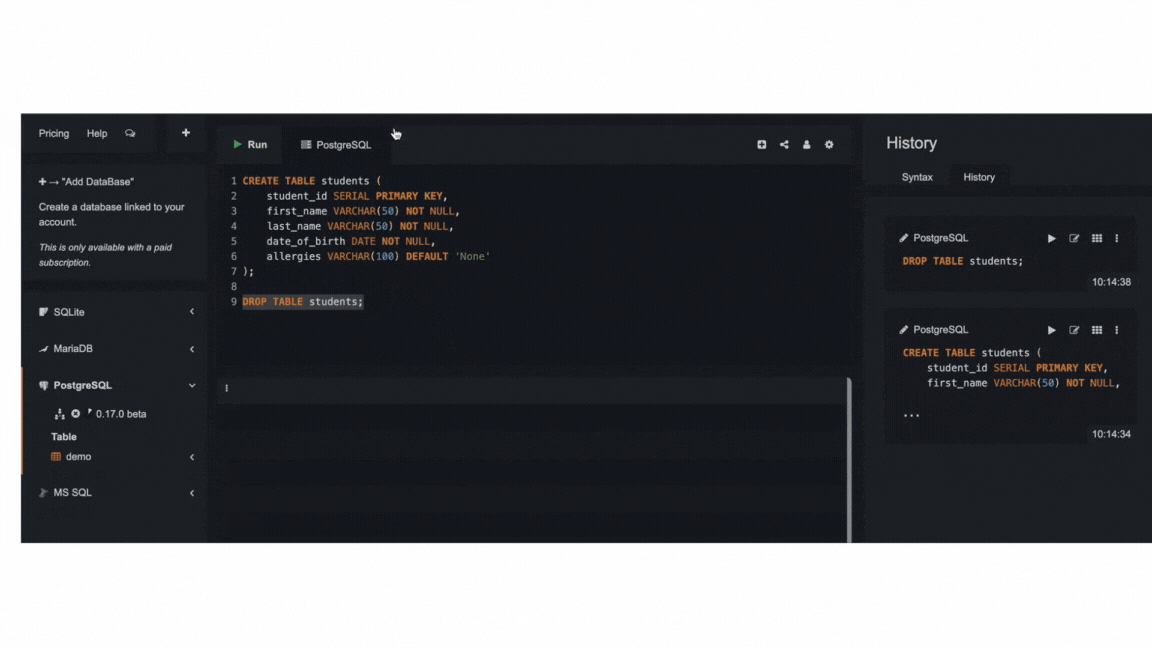
To delete a table, simply use the query below. As usual, be extremely careful when deleting tables and only use it when you're sure about deleting them.
DROP TABLE name_of_table;
In our next lesson, we'll explore how to add data to our table!